[ad_1]
There are three main teams of rotaviruses which trigger diarrhea in pigs they usually embody Rotavirus A, Rotavirus B, and Rotavirus C. Every group of virus is completely different from one another and requires particular assays designed for them. Pig diarrhea usually includes infections with a number of teams of rotaviruses on the similar time.
Assays accessible
Gross pathology

- Evaluates the presence of small gut wall thinning which may recommend the presence of illness.
- Location of lesions: jejunum and ileum
- Professionals:
- Cheap and fast outcomes
- Applies to all three teams of rotaviruses
- Cons:
- Not diagnostic – comparable lesions will be discovered with different illnesses particularly coronavirus infections (transmissible gastroenteritis, porcine epidemic diarrhea, and porcine delta coronaviruses)
- Want contemporary tissues (<15 min) as decomposition dramatically modifications the looks of small gut
- Unable to distinguish between completely different teams of rotaviruses
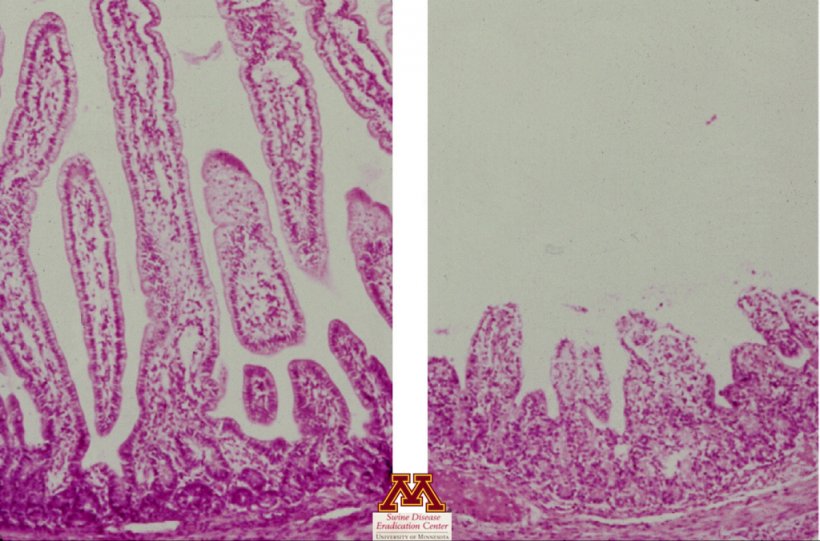
Histopathology
- Evaluates the presence of tissue lesions (small intestinal villus atrophy) which may strongly recommend the presence of illness
- Pattern varieties: jejunum and ileum tissue
- Professionals:
- Affirm villus atrophy suggesting viral enteritis
- Cons:
- Must formalin-fix intestinal tissues inside <15 min of pig loss of life -Intestinal tissue decomposes rapidly
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Detects presence of viral antigen
- Pattern varieties: jejunum and ileum tissue
- Professionals:
- Definitive prognosis: can affirm presence of virus with related lesions
- Cons:
- At present solely accessible for Rotavirus A and Rotavirus C (not accessible for Rotavirus B)
Polymerase chain response (PCR)
- Detects presence of particular sequence of viral nucleic acid (RNA)
- Pattern varieties: jejunum and ileum intestinal tissues, fecal swabs, feces
- Professionals:
- Multiplex PCR can detect completely different rotavirus teams together with Rotavirus A, Rotavirus B, and Rotavirus C
- Excessive sensitivity
- PCR quantification
- Average price
- Can usually do pooling of feces or tissue samples to decrease price whereas minimizing lack of sensitivity (particularly concerning medical relevance).
- Cons:
- Excessive sensitivity – can affirm presence of virus however not illness (excessive prevalence of virus in setting)
Virus isolation
- Isolates stay virus
- Pattern varieties: jejunum and ileum intestinal tissues, fecal swabs, feces
- Professionals:
- Isolate virus to be used in vaccine improvement (autogenous vaccines)
- Cons:
- Costly
- Gradual outcomes
- At present solely accessible for Rotavirus A and never accessible for Rotavirus B or Rotavirus C
- Usually troublesome to develop (many false negatives)
- Sampling dealing with from subject to laboratory can influence virus survival
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Pattern varieties: serum
- Professionals:
- Animals stay constructive for a number of weeks
- Can determine damaging herds
- Cons:
- Excessive prevalence of virus in setting leads to widespread publicity to many/most pigs
- Want assay particular for every rotavirus group
- No cross safety between completely different teams of rotaviruses
Desk 1. Abstract of the relevant assays with respect to the completely different rotavirus teams.
| Rotavirus A | Rotavirus B | Rotavirus C | Can differentiate between teams? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross pathology | Sure | Sure | Sure | No |
| Histopathology | Sure | Sure | Sure | No |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Sure | No | Sure | Sure |
| Polymerase chain response (PCR) | Sure | Sure | Sure | Sure |
| Virus isolation | Sure | No | No | No |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | Sure | No | No | No |
End result interpretation
Gross pathology
- Optimistic: Preliminary affirmation of the presence of intestinal thinning
- Unfavorable: Early or gentle circumstances could not manifest with in depth intestinal lesions
Histopathology
- Optimistic: Affirmation of illness, however not reason for illness
- Unfavorable: Unfavorable, or lesions may have been missed if testing improper pattern or too late after an infection
IHC
- Optimistic: Virus is current at website of lesion
- Unfavorable: Unfavorable, or virus may have been missed if testing happens too late after an infection or the focus of virus is simply too low (solely current for a really quick time period). Doesn’t detect Rotavirus B.
PCR
- Optimistic: Affirmation of presence of the completely different teams of rotaviruses (A, B, and C)
- Unfavorable: Unfavorable, virus may have been missed if testing happens too late after an infection or poor pattern choice or dealing with
Virus Isolation
- Optimistic: Affirmation of presence of virus however not illness
- Unfavorable: Unfavorable, virus may have been missed if testing happens too late after an infection or just unable to develop attributable to different contamination or poor pattern dealing with (current however will be troublesome to tradition). Doesn’t detect Rotavirus B or Rotavirus C.
ELISA
- Optimistic: Previous publicity (> 2-4 weeks) to vaccine or wildtype virus. No affiliation of positivity and illness.
- Unfavorable:
- Unfavorable to vaccine or wildtype virus
- An infection too early to detect
Situations
Neonatal pigs with scours (acute or power)
- Gather fecal samples from 10 or extra untreated scouring pigs and submit for PCR testing for Rotavirus A, Rotavirus B, and Rotavirus C in swimming pools of 5.
- Necropsy of 1-3 not too long ago lifeless or euthanize scouring pigs. Grossly evaluating jejunum and ileum for thinning of intestinal wall and gather samples and place in formalin answer for histopathology and IHC analysis.
Early put up weaning pigs with scours (acute or power)
- Gather fecal samples from 10 or extra untreated scouring pigs and submit for PCR testing for Rotavirus A, Rotavirus B, and Rotavirus C in swimming pools of 5.
- Necropsy of 1-3 not too long ago lifeless or euthanize scouring pigs. Grossly evaluating jejunum and ileum for thinning of intestinal wall and gather samples and place in formalin answer for histopathology and IHC analysis.
[ad_2]

