[ad_1]
Understanding timing of estrous cycle is crucial to bettering reproductive success of your sows
The estrous cycle is the dynamic hormonal cycle that controls replica in feminine mammals in relation to the discharge of eggs (oocytes) and preparation of the uterus for fertilized embryos.
Or to place it shortly, the estrous cycle makes replica attainable!
Whereas a profitable pig operation relies on getting pigs to market, if the breeding herd doesn’t reproduce adequately, then there are fewer pigs accessible to market from the start. Maximizing reproductive efficiency of your herd might require some bother taking pictures if you’re struggling to get sufficient sows or gilts pregnant. There are a large number of the reason why this may occur, nevertheless having a fundamental understanding of what’s taking place through the estrous cycle can help you in figuring out the most effective time to breed your sows, and easy methods to apply synchronization packages if the necessity arises. Right here, we are going to overview the phases of the estrous cycle and spotlight how these modifications can affect replica in your sows.
The timeline
In swine, the estrous cycle usually takes 18-21 days to finish, beginning with commentary of behavioral estrus and ending with the subsequent commentary of behavioral estrus. Throughout this cycle, particular hormone ranges will improve and reduce to facilitate mobile progress, organ improvement, and talk timing of developmental occasions. These hormonal modifications management development of the estrous cycle via the 4 phases of the estrous cycle.
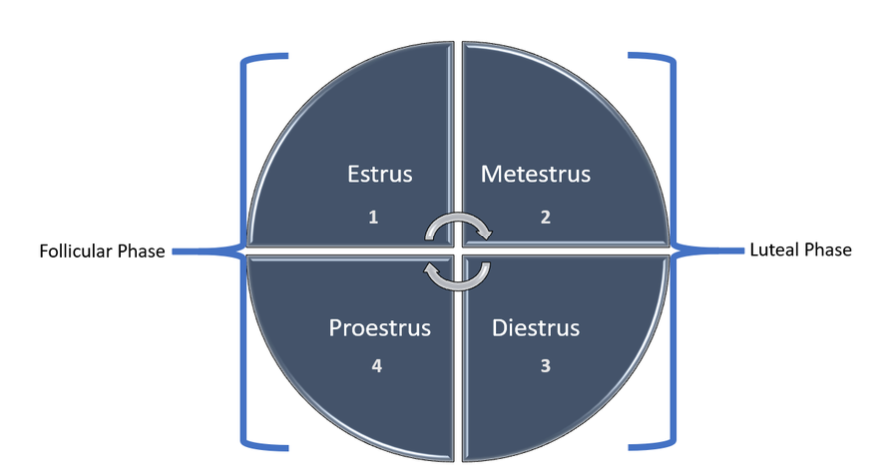
Follicular section
Growing estrogen secretion because the oocyte and follicle mature in direction of ovulation (launch of the egg).
Luteal section
Growing progesterone from improvement of corpus luteum (generally known as the ‘yellow physique’). Section of physiological modifications surrounding the willpower of being pregnant.
Inside every of those phases, there are phases recognized by the precise hormone modifications throughout the section of oocyte and follicle morphology
Follicular Section
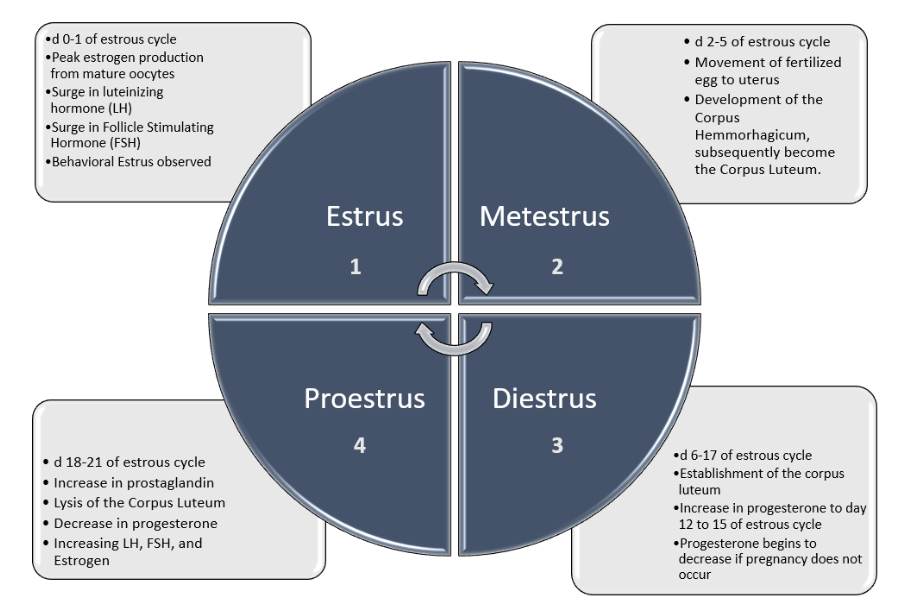
Proestrus (d 17 to 21) stage of follicular section the place estrogen and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) are secreted rising in preparation for estrus. Small pulses of luteinizing hormone (LH) additionally start to be launched.
Estrus (d 0 to 1) stage of follicular section the place oocyte has reached maturity. Estrogen, FSH, and LH secretion peaks, inflicting the follicle to rupture and ovulation to happen. Ovulation sometimes happens inside 24 – 48 hours of peak estrogen launch.
Luteal Section
Metestrus (d 2 to 4) estrogen, LH, and FSH have all declined and the feminine is not sexually receptive to the boar. The ovarian follicles, which launched oocytes throughout ovulation, start the method of luteinization to develop into the corpus hemmorhagicum, after which the corpus luteum. With the formation of the corpus luteum (CL, or ‘yellow physique’) progesterone secretion begins.
Diestrus (d 5 to 18) is the longest stage of the estrous cycle as a result of recognition of being pregnant occurs throughout this section. Throughout this stage, progesterone continues to extend round day 12 of gestation. Right now, the presence of viable embryos will allow being pregnant to persist. If no viable oocytes are detected by day 15 of gestation, prostaglandin F2 alpha (PGF2α) will act upon the CL, inflicting it to regress and scale back secretion of progesterone.
Monitoring the estrous cycle is finest carried out utilizing a calendar. Very like the instance beneath, after behavioral estrus has been noticed, you should use the calendar to estimate timing of hormonal modifications as they relate to the estrous cycle. Based mostly on standing warmth, it is not uncommon for producers to breed sows at 12 hour intervals, beginning 12 hours after the primary noticed standing warmth. Then repeat at 24 hours, and generally 36 hours after the primary noticed standing warmth.
Consciousness of the primary expression of standing warmth and figuring out the period of the estrous cycle is most essential when ordering semen for mating, contemplating the appliance of estrous synchronization protocols or trouble-shooting breeding issues inside your herd. Making use of this fundamental information on physiology of the sow will allow you to raised make the most of instruments accessible for bettering reproductive efficiency of your sow herd.

Headline picture courtesy of A.Ok. Butters-Johnson, Iowa State College
[ad_2]

